Accurate diagnosis of cartilage damage is essential in orthopedic surgery, and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) has significantly enhanced this capability. MRI creates detailed images of internal structures using magnetic fields and radio waves, enabling surgeons to visualize cartilage damage, identify lesions, and plan interventions. This advanced imaging allows for early detection of issues, potentially preventing further progression and facilitating less invasive treatments. Additionally, MRI improves preoperative assessments and surgical planning, ultimately optimizing patient outcomes and ensuring high-quality care.
Importance Of Accurate Diagnosis In Orthopedic Surgery
Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective orthopedic treatment, significantly impacting treatment choices and patient outcomes. Misdiagnosis can lead to prolonged pain and reduced mobility, making comprehensive diagnostics essential, especially for cartilage damage. Advanced imaging techniques like MRI enhance diagnostic capabilities, allowing orthopedic surgeons to visualize intricate structures. This integration improves informed decision-making and fosters a patient-centered approach, ultimately enhancing treatment efficacy and reducing unnecessary procedures and costs.
Understanding Cartilage Damage And Its Impact On Patients
Cartilage is essential for smooth joint movement and shock absorption, protecting bones from wear. Damage can result from aging, injuries, or arthritis, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness that hinder daily activities. This damage may progress to joint instability or osteoarthritis, potentially requiring invasive treatments. Additionally, it can cause psychological distress and reduced productivity, highlighting the need for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention. Understanding the types of cartilage damage helps clinicians tailor treatments, and early detection through advanced imaging like MRI is crucial for preventing further deterioration and exploring conservative options.
Traditional Diagnostic Methods For Cartilage Damage
Assessing cartilage damage has traditionally relied on X-rays and physical examinations. While X-rays can reveal changes in bone structure, they cannot visualize cartilage, limiting their effectiveness. Physical exams help evaluate symptoms like pain and swelling, but their subjective nature can lead to inconsistent diagnoses. This highlights the need for advanced imaging techniques like MRI to provide a detailed understanding of cartilage health, making their integration essential in orthopedic practice.
Limitations Of Traditional Diagnostic Methods
Traditional diagnostic methods like X-rays and physical exams have notable limitations. X-rays cannot visualize soft tissues like cartilage, often leading to missed diagnoses and inappropriate treatment plans. Physical examinations can be subjective, influenced by clinician experience and patient pain tolerance, which may result in misdiagnoses and delayed care. Moreover, traditional imaging often lacks the detail to identify subtle cartilage damage, worsening issues over time. These limitations emphasize the need for advanced imaging techniques like MRI to enhance diagnostic accuracy and guide treatment decisions.
Role Of MRI In Diagnosing Cartilage Damage
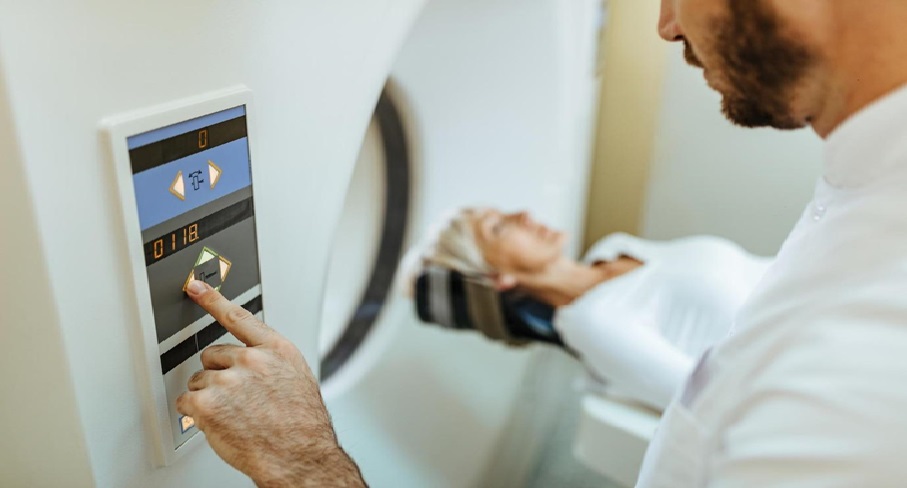
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has transformed orthopedic diagnostics, especially for assessing cartilage damage. Unlike X-rays, MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of soft tissues, enabling the identification of subtle lesions and degenerative changes. Its high-resolution capabilities allow surgeons to differentiate between healthy and damaged cartilage, which is crucial for treatment planning, particularly in conditions like osteoarthritis. Additionally, MRI is non-invasive and free from ionizing radiation, making it safe for patients, including those requiring repeated imaging. MRI at Tellica Imaging provides comprehensive assessments of cartilage damage, leading to better-informed treatment decisions.
Advantages Of Using MRI In Orthopedic Surgery
Integrating MRI into orthopedic surgery dramatically improves patient care by precisely visualizing cartilage damage, enabling early diagnosis and intervention to prevent degenerative conditions. This early detection allows for more conservative treatments, enhancing patient outcomes. MRI’s versatility in assessing various joints—such as the knee, hip, shoulder, and ankle—makes it essential for diagnosing acute injuries and chronic diseases. Additionally, it offers insights into ligaments and tendons, aiding comprehensive assessments. The detailed information from MRI informs surgical planning, allowing surgeons to tailor their approaches and improve surgical outcomes while reducing complications. Overall, MRI enhances diagnostic capabilities and supports better recovery for patients.
Preparing For An MRI for Cartilage Damage Diagnosis
Preparing for an MRI is straightforward but requires some understanding. Patients should discuss their medical history, including any conditions, allergies, medications, and prior surgeries, as metal can interfere with the scan. On the day of the MRI, metallic items must be removed, and patients may wear a provided gown. Staying still is crucial for clear images, and earplugs or headphones may be offered to reduce noise. Those who feel anxious in confined spaces might receive a mild sedative. The scan usually lasts 30 to 60 minutes, with the technologist monitoring from another room. Afterward, patients can typically resume normal activities unless advised otherwise. Knowing these steps helps ensure a smooth MRI experience for diagnosing cartilage damage.
Interpreting MRI Results For Cartilage Damage
Interpreting MRI results requires understanding both imaging findings and clinical context. A radiologist analyzes the MRI and generates a report detailing cartilage condition, lesions, and joint health, which guides treatment decisions. Orthopedic surgeons assess factors like the size and type of cartilage damage to differentiate between localized injuries and degenerative changes, informing treatment options. Correlating these findings with the patient’s symptoms and health status is essential. Effective communication between the radiologist and surgeon clarifies uncertainties, leading to a tailored treatment plan that meets the patient’s needs.
Conclusion And Future Prospects Of MRI in Orthopedic Surgery
In conclusion, MRI has become vital in orthopedic surgery for diagnosing cartilage damage, offering high-resolution images that enhance treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes. Future advancements in imaging techniques and artificial intelligence promise to refine diagnostics further, while ongoing research will better align MRI findings with clinical outcomes. As MRI technology evolves, it is set to revolutionize orthopedic surgery, ensuring high standards of care and enhancing patients’ quality of life.











Comments